

In the first meiotic division parental homologs are disjoined to reduce ploidy to the haploid state, and in the second division, sister chromatids are disjoined. Following synaptonemal complex disassembly during late prophase, homologous chromosomes remain linked by chiasmata, physical attachments provided by crossovers in combination with sister chromatid cohesion. By early pachytene, synaptonemal complex assembly is completed, and by late pachytene, the process of homologous recombination leads to the formation of inter-homolog crossover events. During the transition zone in early meiotic prophase (leptotene and zygotene), homologue pairing is achieved and DSBs are formed. DNA replication occurs at the onset of meiosis.
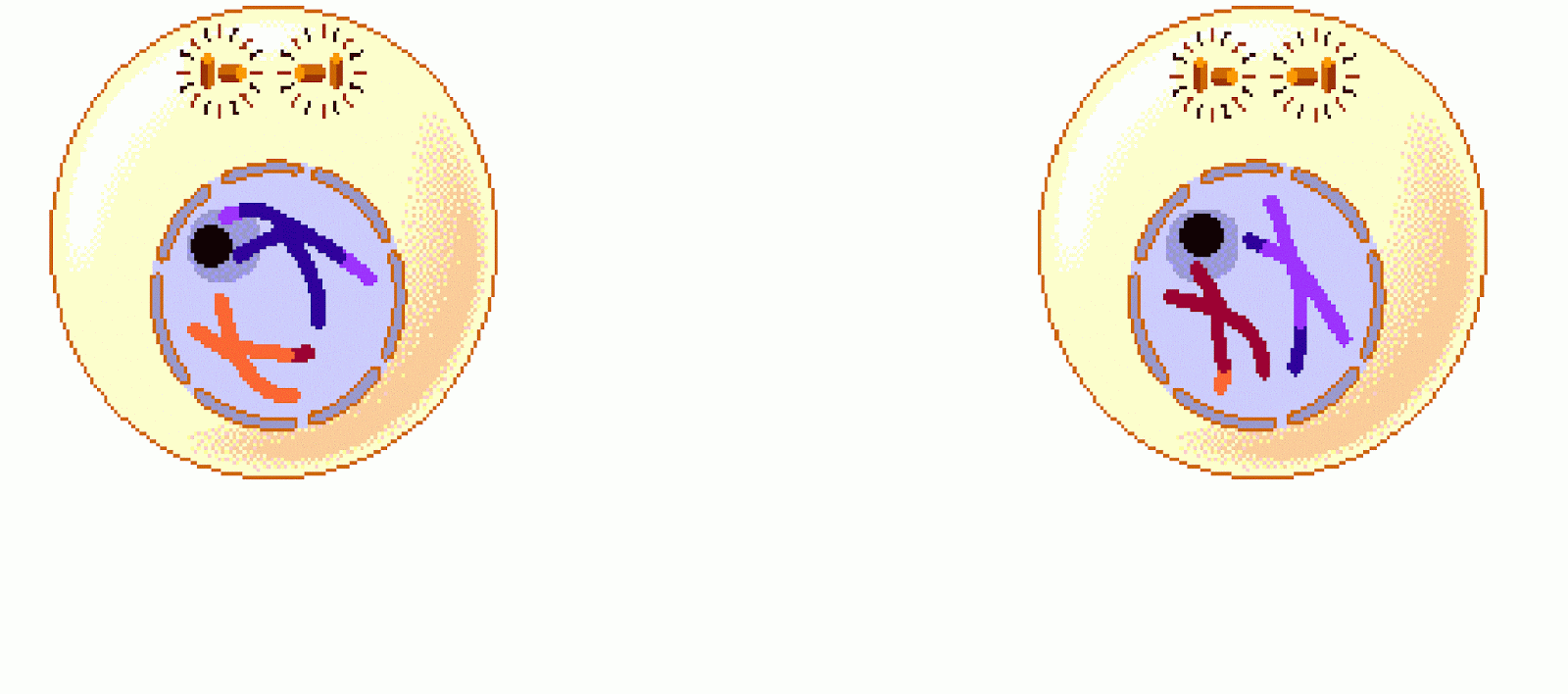
elegans germ lineįor simplicity, a single pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. The separation of sister chromatids on the meiosis II spindle completes the meiotic program.ĭiagram of meiotic events during oogenesis in the C. Late prophase remodeling of chromosome pairs connected by chiasmata results in bivalents wherein the connected homologs are oriented away from each other this promotes bipolar attachment of homologs to the meiosis I spindle, leading to segregation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase I.

Therefore, there are multiple surveillance mechanisms that act to ensure that each homolog pair undergoes an exchange. Crossing over is essential for the formation of chiasmata, connections between homologs that become evident upon structural remodeling of chromosomes during later stages of meiotic prophase (diplotene and diakinesis). Crossover (CO) recombination events must be completed between the DNA molecules of the aligned and synapsed homologs, a process started by the deliberate formation of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs).
PROPHASE 1 OF MEIOSIS FULL
During the zygotene stage, a specialized protein structure called the synaptonemal complex (SC) assembles between the aligned chromosomes to hold homologs together full synapsis of homologs defines the pachytene stage. During early prophase (leptotene and zygotene stages), each chromosome must locate and recognize its appropriate homologous pairing partner and align with it. This reduction in ploidy is essential to ensure the restoration of diploidy upon fertilization and requires completion of several key events ( Figure 1). Sexual reproduction requires the generation of haploid gametes from diploid precursors through the specialized cell division program of meiosis. We also review the regulatory processes that ensure the coordinated execution of these meiotic events during prophase I. In this chapter, we review the seminal events of meiosis: pairing of homologous chromosomes the changes in chromosome structure that chromosomes undergo during meiosis the events of meiotic recombination the differentiation of homologous chromosome pairs into structures optimized for proper chromosome segregation at Meiosis I and the ultimate segregation of chromosomes during the meiotic divisions. elegans (and most other eukaryotes) homologous pairing and recombination are required for proper chromosome inheritance during meiosis accordingly, the events of meiosis are tightly coordinated to ensure the proper execution of these events. During the second meiotic division, which is similar to mitosis, sister chromatids separate the resultant products are haploid cells that become gametes. These crossovers, in conjunction with sister chromatid cohesion, serve to connect the two homologs and facilitate their segregation to opposite poles during the first meiotic division. In preparation for the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes pair and synapse, creating a context that promotes formation of crossover recombination events.
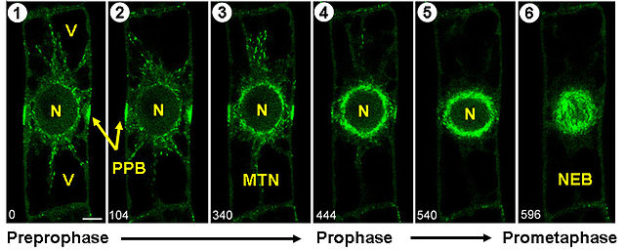
This reduction in genetic content is accomplished during a specialized cell division called meiosis, in which two rounds of chromosome segregation follow a single round of DNA replication. Sexual reproduction requires the production of haploid gametes (sperm and egg) with only one copy of each chromosome fertilization then restores the diploid chromosome content in the next generation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
